Introduction
Data quality in clinical research refers to the reliability and accuracy of qualitative or quantitative information collected during studies. High data quality ensures reliable research findings and avoids incorrect conclusions and recommendations. Errors in data can significantly impact the outcomes of clinical trials, making it essential to prevent data errors during the development, design, and collection phases. This blog explores the factors contributing to good data quality, the processes involved in Data Quality Management (DQM), and the strategies for reducing errors in clinical research.
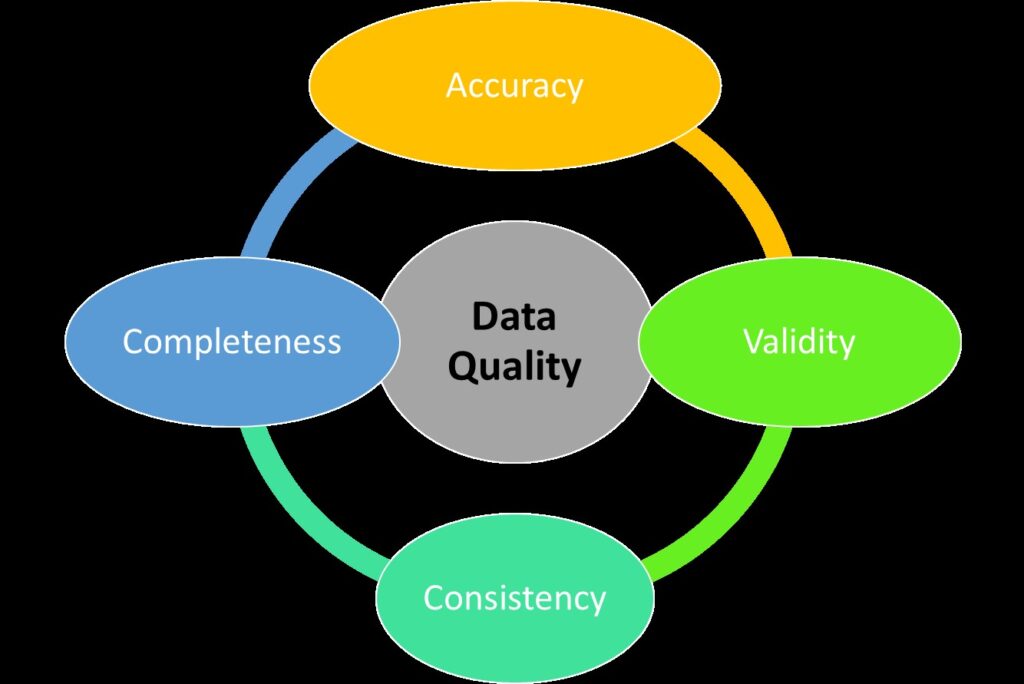
To ensure high data quality, several factors must be considered:
- Accuracy: Data must reflect the true situation of the research subjects.
- Completeness: All necessary data should be collected to achieve the research objectives.
- Consistency: Data should be consistent and coherent across various datasets and sources.
- Timeliness: Data should be up-to-date and available when needed.
- Understandability: Data should be easy for the intended users to comprehend.
- Validity: Data should conform to the research protocols and regulatory standards.
Data Quality Management (DQM)
DQM is a formal process that manages the quality, validity, and integrity of research data from collection to analysis and publication. DQM involves:
- Quality Assurance (QA): Ensures that data collection and processing follow the established standards and protocols.
- Quality Control (QC): Involves regular checks and validations to detect and correct errors.
DQM begins with a Data Management Plan (DMP), specified in the study protocol and approved by Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) and sponsors before the study commences.
Components of DQM
- Regulatory File: Organized and retained documentation supporting monitoring and auditing by regulatory bodies.
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Established procedures for conducting clinical trials.
- Personnel Training: Ensuring staff are trained to follow protocols accurately.
- Data Monitoring: Regular checks on data collection and processing.
- Design of Case Report Forms (CRFs): Ensuring CRFs are well-designed to capture necessary data accurately.
Strategies for Reducing Errors
To minimize errors in clinical research data, several strategies and interventions are implemented, including:
- Development and adherence to SOPs.
- Comprehensive training programs for personnel.
- Regular data monitoring and audits.
- Rigorous design and testing of CRFs.
Adherence to Guidelines
International and national guidelines emphasize the importance of data quality and assurance in clinical research. Key guidelines include:
- ICH GCP E6(R3): Guidelines for good clinical practice in trials.
- ISO Standards: Clinical investigation standards for medical devices and quality management systems.
Solutions at Pomat Health
At Pomat Health, we prioritize high-quality data as the foundation of successful clinical trials. As a trusted Contract Research Organization (CRO), we ensure the integrity, accuracy, and reliability of data, enabling sponsors to make informed decisions. Our rigorous quality control processes, standardized procedures, advanced data management systems, and adherence to global regulatory requirements help avoid costly delays and drive successful trial outcomes.
Partner with Us
Partner with Pomat Health to ensure data quality excellence, drive reliable outcomes and advance healthcare innovation.
References
- Said, Ayman & Said, Ayesha. (2023). Data Governance Strategies for Data Quality and Integrity in Clinical Trials.
- Sasidhar, D. (2023). Data Integrity and Risk. Open Journal of Optimization, 12(02).
Leave a Reply